Managing Cervical Dystonia: Best Treatment Approaches
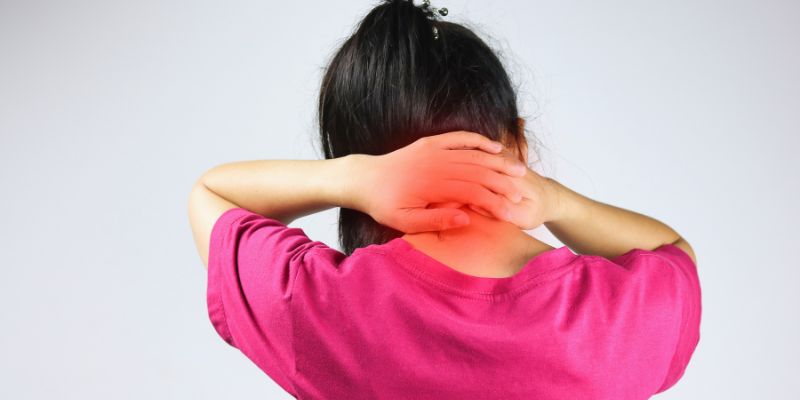
Cervical dystonia or spasmodic torticollis is a rare neurological disease that induces uncontrollable muscle contraction in the muscles of the neck, resulting in abnormal postures of the head and chronic pain. Treatment of the disease positively affects the life quality of patients. This article explains the optimum treatment methods of cervical dystonia, including medical treatments, physical therapies, and lifestyle modifications. Through the awareness of the process, readers possess the power of making suitable choices in a way to manage symptoms more suitably and enhance living.
Understanding Cervical Dystonia
Cervical dystonia, a painful and chronic movement disorder, is a miscommunication between the brain and the neck muscles that leads to involuntary postures or movements. The etiology of the condition has not yet been established, but it is believed to be a mix of genetic and environmental factors, with some of the origins being traced to family history.
The condition most frequently occurs in middle-aged adults, but it can happen to anyone at any age. Cervical dystonia is not a life-threatening condition, but the impact of the condition on mobility and daily living is significant.
Symptoms and Diagnosis

Cervical dystonia presents with a range of symptoms that may differ in severity between patients. Typical signs and diagnostic features include:
- Neck pain: Usually an initial symptom, ranging from mild to severe pain.
- Abnormal head posture: Sidelong twisting or tilting of the head or pulling the head to the back.
- Tremors: Rhythmic head shaking in some patients.
- Muscle stiffness: Shoulder and neck muscles' rigidity.
- Exacerbation by stress: Symptoms may be worsened by anxiety or fatigue.
Best Treatment Options
Cervical dystonia can be treated with multiple therapies specific to a case. The most helpful treatment modalities for cervical dystonia are listed below:
1.Botulinum Toxin Injections
Botulinum toxin injections are the initial treatment of choice for cervical dystonia. The treatment involves injecting small doses of botulinum toxin directly into the affected neck and shoulder muscles to temporarily prevent nerve impulses causing the muscle spasms. By doing so, it effectively relieves abnormal movement, tremors, and muscle stiffness of the condition.
The effects last for three to four months, and repeated injections can be required subsequently. The treatment is well tolerated, with minimal side effects such as localized pain or mild weakness of the injected muscle. Adding botulinum toxin injections to physical therapy or stretching exercises can also further enhance symptom relief and quality of life in patients.
2.Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a part of the treatment of movement disorders and musculoskeletal diseases. It increases mobility, relieves pain, and overall function. Physical therapy is tailored to the patient's needs and includes certain exercises and interventions to treat affected muscles and joints. With regular visits to a trained therapist, remarkable improvements in strength, flexibility, and coordination can be made. Physical therapy is also combined with other treatments, such as botulinum toxin injections or medications, to provide complete care.
Key benefits of physical therapy include:
- Greater strength and mobility of muscles and joints, allowing you to move and manage daily activities more easily.
- Improved posture and balance, reducing your risk of falls and improving body alignment for general improved body health.
- Reduced tightness and spasticity of muscles, reducing tension and pain to improve comfort and mobility.
- Improved coordination and mobility, allowing more controlled fluid motion and increased independence.
- Improved long-term symptom control and rehabilitation support, providing you with the tools and exercises to further improve recovery and maintain improvement over the long term.
3.Oral Medications
Oral drugs also play an important role in symptom control, especially for symptoms such as spasticity and movement disorders. Oral drugs achieve this by acting on specific pathways of the nervous system to relax contractured muscles, decrease pain, and enhance mobility. Oral drugs are usually combined with other therapy such as physical therapy for optimal benefit. The best drug and dosage should be consulted with a doctor, as it would be prescribed on an individual basis depending on the individual's requirements.
Key benefits of oral medications include:
- Reduced muscle spasticity and rigidity, allowing patients to move more freely and perform daily activities with greater ease and confidence.
- Improved motor function and movement, helping patients complete tasks with greater precision and control, boosting their independence in daily life.
- Less pain and discomfort from muscle tightness, offering significant relief and improving overall comfort levels, which can contribute to better mental well-being.
- Improved quality of life through effective symptom management, allowing patients to fully engage in work, hobbies, and social activities without constant limitations.
- Personalized dosages tailored to each patient, ensuring better results, fewer side effects, and a safer, more effective treatment.
4.Stress Management
Stress management plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being, particularly for individuals dealing with chronic conditions. Effective stress management techniques can reduce stress levels, helping to ease muscle tension and improve both mental and physical health. Strategies such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and physical activities like yoga can promote relaxation and enhance mood.
Maintaining a balanced lifestyle with proper sleep, a healthy diet, and consistent routines can further support stress management. Seeking professional help or joining support groups can be beneficial for those struggling with high stress levels, fostering resilience and emotional stability.
5.Surgery
Surgery may be considered for severe cases of cervical dystonia that do not respond to other treatments. Surgical options often focus on interrupting the nerve signals responsible for the abnormal muscle contractions. One common procedure is deep brain stimulation (DBS), which involves implanting a device that sends electrical impulses to specific areas of the brain. Another option might include selective peripheral denervation, where targeted nerves are cut to alleviate symptoms.
Key points about surgical treatment include:
- Surgery is usually for severe cases that don’t respond to medication or other treatments.
- Procedures like deep brain stimulation (DBS), which implants electrodes in the brain to regulate abnormal activity, can offer long-term relief for certain conditions.
- Selective peripheral denervation, which cuts specific nerve pathways, may help reduce unwanted muscle contractions or abnormal movements.
- Rehabilitation, including physical therapy and monitoring, is often needed for the best recovery and outcomes.
Conclusion
Surgical treatments for movement disorders offer hope to patients with severe symptoms that don't respond to other methods. Procedures like deep brain stimulation and selective peripheral denervation can greatly improve quality of life but are typically reserved for those with limited options. Success relies on comprehensive care, including rehabilitation and monitoring to support recovery. When carefully considered and performed with proper clinical guidance, surgery can be life-changing, providing renewed independence and stability. Patients should consult medical professionals to determine the best course of action.